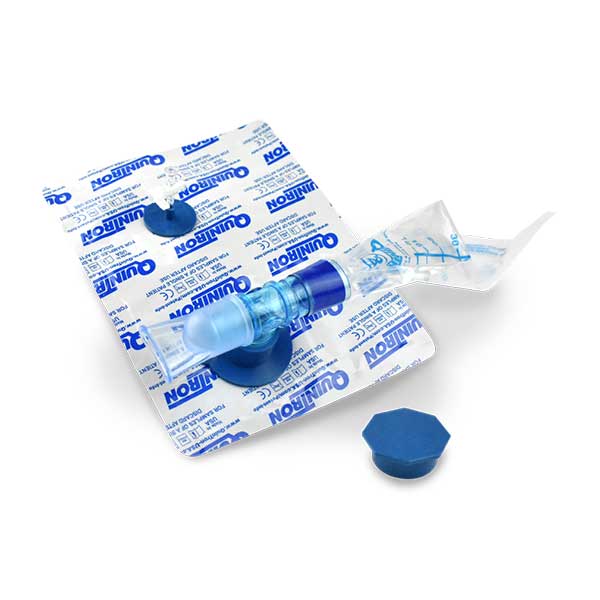
Breath Testing for digestive disorders
Breath Analyzers and Kits
Breath Analyzers
Simple. Accurate. Reliable. Discover QuinTron breath analyzers: trusted by thousands of hospitals, clinics, and laboratories around the world. Measure trace hydrogen and methane concentrations to better serve patients seeking digestive wellness.
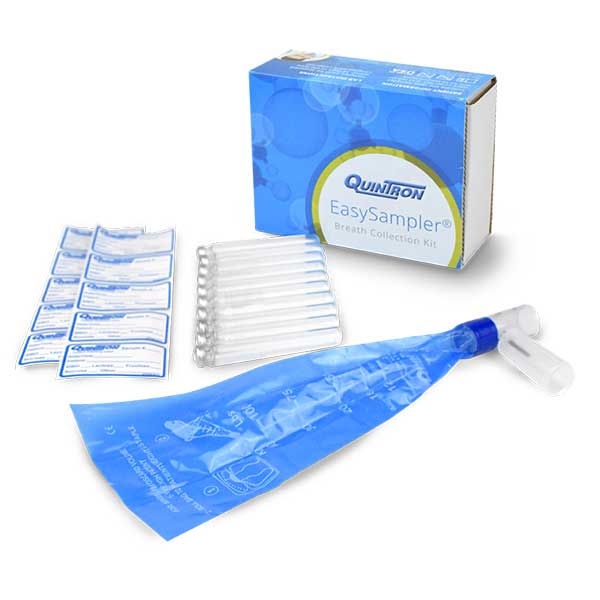
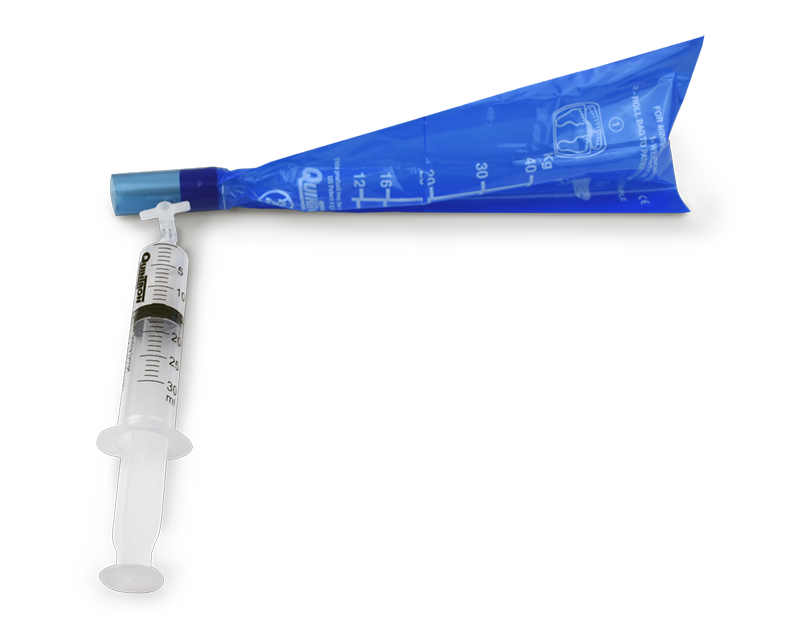
Breath Testing Kits
QuinTron's range of patented breath testing products allows for economical and flexible solutions for both in-office and at-home testing. Provide your patients with convenience and help them find the answers they seek in their search for digestive wellness.
IBS and related GI disorders are painful and inconvenient – reducing patients' quality of life.
Due to gut microbiome dysbiosis, patients with IBS may have increased intestinal permeability, dysmotility, chronic inflammation, autoimmunity, decreased absorption of bile salts, and even altered enteral and central neuronal activity. Consequently, SIBO and IBS share many symptoms including abdominal pain, distention, diarrhea, and bloating. Getting diagnostic answers can be as easy as a QuinTron breath test.
With a simple breath test, you may be able to discover that Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO), Intestinal Methanogen Overgrowth (IMO), and/or carbohydrate malabsorption are causing your patient's IBS symptoms. Proper diagnosis leads to treatment success.
Breath Tests Detect Gastrointestinal Disorders, Including:
-
Carbohydrate malabsorption
-
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)
-
Intestinal Methanogen Overgrowth (IMO)
The breath testing process is simple, convenient, and non-invasive. Breath testing is much less expensive and less invasive than other diagnostic tests like endoscopy and colonoscopy. It's a simple first step to identify or rule out digestive issues such as Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO), Intestinal Methanogen Overgrowth (IMO), or carbohydrate malabsorption.
QuinTron's range of breath test analyzers and breath testing kits offer flexibility to hospitals and clinics by providing in-office and at-home collection options.
Purchase an analyzer
Practitioners can analyze breath samples immediately by purchasing their own QuinTron analyzer. Thousands of hospitals, clinics, and laboratories worldwide trust and use our analyzers. Breath tests may be reimbursable under CPT 91065 ("Breath Hydrogen Test").
QuinTron's world-class analyzers and collection systems are made in the U.S.A and rigorously tested for accurate, repeatable results. Measure trace gas concentrations of Hydrogen and Methane using state-of-the-art techniques. Our solid-state sensors, unlike electrochemical sensors, don't lose sensitivity or require regular replacement.
We designed our patented collection kits to reduce the risk of external contamination, preventing the loss of sample integrity.
Contact us for a free consultation. Our knowledgeable team will help you determine the best options to fit your needs and the needs of your patients.
Work with one of our analysis partners
Request a supply of breath collection kits. Healthcare professionals may request a supply of QuinTron breath collection kits to stock in-office without investing in additional equipment. Keep a ready supply on hand for simple, fast testing when your patients need it the most.
When you contact us to request a supply of breath test kits, we'll explain program options to you and help you set up to receive tests at your clinic or office. Patients will receive a test kit from you so that you can review the collection process with them. Patients will then ship back their test to one of our partners for analysis.
Analysis results are typically available within 72 hours after receipt by the analysis team, allowing you to discuss and review results with your patient quickly. This fast rate of return will enable you to explore potential courses of treatment right away.
Patient-direct collection kits
Refer your patients to QuinTron’s online store to order a breath collection kit for personal use. Once your patient orders the kit, we will handle the steps from there.
- We will ship the breath test kit directly to the patient for easy and convenient testing in the privacy of their home or office. *
- After the patient returns samples to us using the prepaid shipping label in their kit, one of our partners will perform the analysis and provide the results.
Patients will typically receive their results within 72 hours once the analysis team receives their sample and test kit. You will be able to reconvene with your patient after testing to discuss a follow-up plan for care and the potential course of treatment. Help your patients get the answers they need privately, conveniently, and quickly.
*Excludes kits that may contain prescription drugs (i.e., lactulose). See the online store for details or contact our representatives for more information.
Research-Based Testing Methodology
QuinTron's products and methodology are referenced in over 100 research articles and studies.
According to Hydrogen and Methane-Based Breath Testing in Gastrointestinal Disorders: The North American Consensus:
“A recent retrospective study of subjects undergoing concurrent glucose breath testing with scintigraphy concluded that glucose breath testing has a high false-positive rate due to arrival of the scintigraphy in the cecum prior to a rise in hydrogen or methane on testing.”
For greater accuracy, North American medical practitioners prefer lactulose-based breath testing.
In Methodology and Indications of H2-Breath Testing in Gastrointestinal Diseases: The Rome Consensus Conference, a panel of practitioners cited the effectiveness of lactulose-based breath testing:
“GBT seems to have a higher diagnostic accuracy in studies comparing breath tests versus culture.”
Citing two different substrate doses and testing periods, the panel concludes, “The diagnostic accuracy is around 70% for both tests.”
Why Provide QuinTron's Breath Tests to Your Patients?
Breath testing is a first-line diagnostic tool.
Trace gases measured in exhaled breath offer insights into fermentation processes in the digestive system and have shown to cause various types of functional issues affecting nearly all of the body's systems.
The trace gases measured with our analyzers are Hydrogen (correlated with IBS-D), Methane (correlated with IBS-C and IBS with mixed bowel habits).
Additionally, our analyzers have built-in quality control features to determine the validity of each sample and ensure accuracy. Breath testing is much less expensive and less invasive than other diagnostic procedures such as colonoscopy or endoscopy, making it a low-cost, reliable first option.
Breath testing doesn’t always require an office visit.
In response to COVID-19, hundreds of offices have enrolled and switched in-office testing to QuinTron's patented at-home breath test collection kits to limit patient interaction and free staff for other duties.
Patients safely and privately collect samples at home and drop them off or ship them to your office or a lab for analysis. We designed our collection vials specifically for breathing samples, ensuring the samples remain stable for up to 14 days, allowing greater access to patients in remote locations worldwide.
Discover the Advantages of Breath Testing

Low Cost
Compared to more invasive procedures, such as endoscopic procedures, QuinTron offers high-quality, low-cost diagnostic tests as a wise first step to narrow down the potential cause of digestive issues.
Convenient
Whether you're a healthcare professional exploring testing for office use or someone seeking to purchase your own test, QuinTron has multiple convenient options for in-office and patient-direct testing.
Fast
QuinTron's network of breath analysis partners typically provides results within 72-hours from the receipt of samples. This quick turnaround will help you develop an immediate comprehensive treatment plan.
*QuinTron is a medical device manufacturer and is not able to provide patient referrals, medical advice, interpretation/diagnosis of results, or insurance coverage information. However, we are happy to provide additional references and guidance on properly collecting breath samples and using our products.






Safety And Quality Are Non-Negotiable
We Pride Ourselves with Our High Standards
FDA # 2124914
Registered & Certified
ISO 13485
Ensuring Best Practices In Everything We Do
Certificate MDSAP 671378
Certificate FM 671377